brittle material compression testing|What is Compression Testing? : purchase Recently, some works have shown that it is possible to characterize and find the constitutive equation for brittle materials using a confined compression test, i.e., a test where a cylindrical specimen, surrounded by a confining sleeve, is being compressed axially by a mechanical testing machine. Nuevo chat de QuieroChat.Com. Chatea y haz amistades de todo el mundo en el chat de QuieroChat.Com
{plog:ftitle_list}
web6 dias atrás · Lotofácil. Federal. Loteca. Dia de Sorte. Timemania. Super Sete. + Milionária. PUBLICIDADE. Fonte: Caixa Econômica Federal. Resultado | Concurso 3037 .
Compression tests are used to determine a material’s behavior under applied crushing loads, and are typically conducted by applying compressive pressure to a test specimen (usually of either a cuboid or cylindrical geometry) using .

Tensile Testing distribution
Recently, some works have shown that it is possible to characterize and find the constitutive equation for brittle materials using a confined compression test, i.e., a test where a cylindrical specimen, surrounded by a confining sleeve, is being compressed axially by a mechanical testing machine.Brittle materials in compression will have an initial linear region followed by a region in which the shortening increases at a higher rate than does the load. Thus the compression stress-strain diagram has a shape that is similar to the .In a compression test, there is a linear region where the material follows Hooke's law. . Otherwise, if the material is ductile yielding usually occurs which displaying the barreling effect discussed above. A brittle material in .

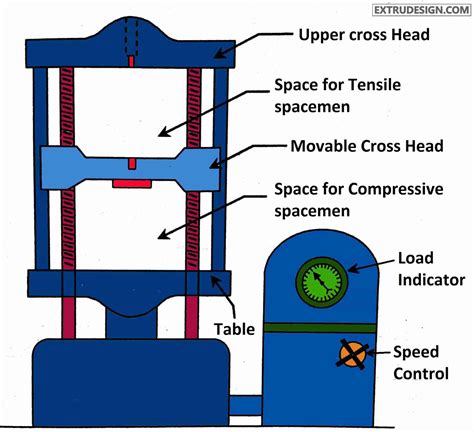
What is Compression Testing?
Materials lacking this mobility, for instance by having internal microstructures that block dislocation motion, are usually brittle rather than ductile. The stress-strain curve for brittle materials are typically linear over their full range of strain, eventually terminating in fracture without appreciable plastic flow. Brittle failure limits the compressive strength of rock and ice when rapidly loaded under low to moderate confinement. Higher confinement or slower loading results in ductile failure once the .
Compression testing is used more often for brittle materials. For compression testing, an electromechanical testing machine is also used to determine the material properties upon the application of a compressive load (Fig. 1 B) and compressive stress–strain curves are recorded. Properties such as compressive modulus and compressive strength . A reasonable expectation would be that the failure angles will vary from zero degrees (splitting) for a very brittle material in uniaxial compression to 90° (fracture) for a very brittle material in uniaxial tension. . This kind of failure is common in geology , and in the laboratory testing of geological materials . The compressive . Brittle materials are generally weak in tension but strong in compression. Hence this test is normally performed on cast iron, cement concrete etc. But ductile materials like aluminium and mild steel which are strong in tension, are also tested in compression. . For compression test, we can Compression test is preferable to tension test for brittle materials. Compression test becomes essential for ductile materials which undergo more than 50% plastic strain during mechanical working processes. Pure compressive stress causes to push the atoms in a material closer together, which obviously cannot produce failure of a homogeneous non .
Compressive strength of concrete
Compressive Testing
On the other hand, the study of size effect for concrete and other “quasi-brittle” materials is relatively new, even less than fifty years [1]. Even for the size effect in concrete, it was studied for tension and flexure in most of the literature. . For compression testing, a cylinder yields more consistent results than a cube, given that .
Granite is a hard and brittle material. The failure process is violent in the uniaxial compression test under axial strain control mode. In order to protect the extensometer from damage, only the .
Material compression testing can be divided into two forms depending on the speed of the test: Static and dynamic modes. . When compression testing CMCs, due to the very brittle ceramic matrix, it is necessary to ensure good surface contact between the sample and the compression plates. Point or line contacts and uneven pressure can produce .
Uniaxial compression tests were conducted on quartz mica schist in a laboratory to study the brittle failure modes of foliated rocks. By focusing on the crack evolution pattern, the failure mechanisms of foliated rocks were investigated by numerical tests based on particle discrete element theory. Furthermore, the effect of fabric on the mechanical anisotropy of . Since Griffith was put forwarded the energy criterion for crack propagation in brittle materials, a large number of studies on viscous-elastic materials rheological failure were conducted.Knauss and Dietmann proposed the criterion for the critical value of unstable crack propagation in viscoelastic body and Griffith’s energy criterion was extended to time .Factors Affecting Ductility & Brittleness. Several factors can affect the ductility and brittleness of a material, including: Temperature: As mentioned earlier, temperature plays a crucial role in determining the ductility and brittleness of a material. At high temperatures, materials are typically more ductile, while at low temperatures, they tend to become more brittle. It appears that the investigation of the damage process provided physical insight into damage accumulation and failure of rocks in compression. For brittle materials subject to arbitrary stresses, a CDM model was developed by considering a dilute distribution of non-interacting fiat microcracks which self-similarly propagate in a linear elastic .
Newman and Lachance (1974) performed a detailed study of the uniaxial compression test for brittle materials after commenting on the validity of the standard test. They stated that for the compressive strength test results to be used to examine the fundamental properties of concrete, independent of the testing method, one of three conditions . Full, general characterization of the behaviour of brittle materials under compression has eluded the scientific community. For example, the broad diversity of failure theories for masonry under different loads illustrates this situation well. . Shrive N (1983) Compression testing and cracking of plain concrete. Mag Concr Res 35(122):27–39 .
5.2 Use— Compressive properties are of interest in the analyses of structures subject to compressive forces or bending moments or both and in the analyses of metal working and fabrication processes that involve large compressive deformation such as forging and rolling. For brittle or nonductile metals that fracture in tension at stresses below the yield strength, . The inclusion plays a crucial role in mastering mechanical responses and cracking behaviors of brittle materials. In this work, a series of uniaxial compression tests were performed to investigate the effect of infilling composition (i.e., proportion and grain size) on the mechanical responses of brittle materials. Digital image correlation (DIC) and acoustic .
With a brittle material, tensile testing may give an approximately linear stress-strain plot, followed by fracture (at a stress that may be affected by the presence and size of flaws). . (These two materials will also be used to illustrate some effects concerned with compression and indentation testing.) The L-H law is being used here, with . Brittle materials will, in general, fracture, as the elastic limit is exceeded, as bulging can only occur if ductility is present. . Compression Test: Compression testing loads a standardized test block axially, with pure compressive force, which tends to shorten the sample in the compressive axis and bulge the sides, making a complex load . The micromechanics of brittle failure in compression and the transition from brittle to ductile failure, observed under increasing confining pressures, are eaxamined in the light of existing .
Understanding the size dependence of quasi-brittle materials' fracture behavior is useful in assessing the safety of flawed rock engineering structures. In this study, a set of uniaxial compression tests were conducted to scrutinize the mechanical properties and crack morphology of cubic specimens with sizes of 75 mm, 100 mm, 125 mm and 150 mm. The results showed .
Compression Test Of Concrete: The Ultimate Guide To
In the equation for stress, P is the load and A 0 is the original cross-sectional area of the test specimen. In the equation for strain, L is the current length of the specimen and L 0 is the original length. Stress-Strain Curve. The values of stress and strain determined from the tensile test can be plotted as a stress-strain curve, as shown below:for ductile materials, asymmetric response in tension-compression for brittle materials with higher strength in compression, no plastic yielding, etc. . Readings: BC 2.3 117. 118 MODULE 5. MATERIAL FAILURE (a) test y y E 1 (b) Ductile (c) Brittle Figure 5.1: Uni-axial stress-strain response for ductile and brittle materials. Test setup. In the bending flexural test, a specimen is loaded under uniaxial bending stress (tension and compression) in order to obtain information on the bending behaviour of materials.Especially brittle materials such as hard metals, tool steels and grey cast iron are tested in flexural tests. In such a bending test flexural strength, deflection at fracture .
webI. Introducción. El 30 de octubre de 2023, la secretaría recibió una petición del Brasil para que se incluyera un tema en el programa provisional del 28o período de sesiones de .
brittle material compression testing|What is Compression Testing?